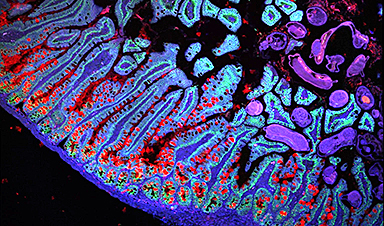
New research from the Human Cell Atlas offers insights into cell development, disease mechanisms, and genetic influences, enhancing our understanding of human biology and health.
The Human Cell Atlas (HCA) consortium has made significant progress in its mission to better understand the cells of the human body in health and disease, with a recent publication of a Collection of more than 40 peer-reviewed papers in Nature and other Nature Portfolio journals.
The Collection showcases a range of large-scale datasets, artificial intelligence algorithms, and biomedical discoveries from the HCA that are enhancing our understanding of the human body. The studies reveal insights into how the placenta and skeleton form, changes during brain maturation, new gut and vascular cell states, lung responses to COVID-19, and the effects of genetic variation on disease, among others.
Contributed by researchers worldwide, the papers in the Collection serve as essential tools and examples for building cell atlases on a large scale. Collectively, they demonstrate the HCA's commitment to capturing the full spectrum of human diversity, including genetic, geographic, age, and sex differences.

Comprehensive Mapping of Human Cells
The HCA is developing and using experimental and computational approaches in single-cell and spatial genomics to create comprehensive reference maps of all human cells—the fundamental units of life—as a basis for both understanding human health and diagnosing, monitoring, and treating disease. To date, more than 3,600 HCA members from over 100 countries have worked together to profile more than 100 million cells from over 10,000 people. Researchers are currently working to assemble a first draft Human Cell Atlas, which will eventually grow to include up to billions of cells across all organs and tissues.

New Insights from the HCA Collection
This Collection of studies in Nature Portfolio demonstrates major advances in three aspects of HCA's mission: mapping individual adult tissues or organs, mapping developing human tissues, and developing groundbreaking new analytical methods, including artificial intelligence/machine learning-based methods. The researchers involved are members of the 18 Biological Networks of the HCA, each of which is focused on a particular organ, tissue, or system.

Foundational Goals and Achievements of HCA
"The Human Cell Atlas is a global initiative that is already transforming our understanding of human health. By creating a comprehensive reference map of the healthy human body—a kind of 'Google Maps' for cell biology—it establishes a benchmark for detecting and understanding the changes that underlie health and disease. This new level of insight into the specific genes, mechanisms, and cell types within tissues is laying the groundwork for more precise diagnostics, innovative drug discovery and advanced regenerative medicine approaches," said Professor Sarah Teichmann, founding co-chair of the Human Cell Atlas, now at the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute.

Enhancing Our Understanding of Human Biology
Dr. Aviv Regev, founding co-chair of the HCA, now at Genentech, said: "This is a pivotal moment for the HCA community as we move towards achieving the first draft of the Human Cell Atlas. This collection of studies showcases the major advances from biology to AI achieved since the publication of the HCA White Paper in 2017 and that now deliver numerous biological and clinical insights. This large-scale, community-driven, globally representative, and rigorously curated atlas will evolve continuously and remain accessible to all to advance our understanding of the human body in health and treatments for disease."

Detailed Insights into Human Tissues and Disease
Several studies in the Collection provide a detailed analysis of specific tissues and organs and reveal new biological discoveries important for understanding disease. For example, a cell atlas of the human gut from healthy and diseased tissue identified a gut cell type that may be involved in gut inflammation [Oliver et al.], providing a valuable resource for investigating and ultimately treating conditions such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Developmental Biology and Genetic Insights
The new collection of papers also includes novel maps of human tissues during development. These include the first map of human skeletal development, revealing how the skeleton forms [To et al.], shedding light on the origins of arthritis, and identifying cells involved in skeletal conditions. An additional study describes a multi-omic atlas of the first-trimester placenta, including insight into genetic programs that control how the placenta develops and functions to provide nutrients and protection to the embryo [Shu et al.]. These and other developmental biology studies in the Collection increase our fundamental understanding of healthy development in time and space and provide blueprints and resources for creating therapeutics since many diseases originate in human development.
Promoting Equity and Ethical Research
An accompanying article highlights the importance of including samples from historically underrepresented human populations and describes actions and principles aimed at promoting equitable science
Professor Partha Majumder of the John C Martin Centre for Liver Research and Innovation, India, and a member of the HCA Organizing Committee member and Co-Chair of the HCA Equity Working Group, said: "A key priority for HCA is to ensure a representation of the vast range of human diversity; genetic, cultural and geographical. HCA studies such as the Asian Immune Diversity Atlas and the analysis of distinctive histopathological differences in COVID-19 samples from Malawi demonstrate the remarkable power of large-scale international scientific collaboration."
Another article illustrates HCA's role in developing new ethical guidance on a broad range of issues in genomic science and making this advice available to scientists worldwide [Kirby et al.].
AI Revolutionizing Cellular Biology Research
Just as AI has revolutionized humans' ability to process text quickly, it is also now helping scientists to develop a deeper and more complete understanding of biology at the cellular level and beyond. The Collection introduces new AI methods to better understand and classify cell types and search for cells in this vast map. For example, SCimilarity [Heimberg et al.] enables researchers to compare single-cell datasets to identify similar cell types in different tissues and contexts, analogous to how "reverse image search" can search for photos. Other research teams tackled long-standing challenges, such as classifying cells into hierarchical groups based on their properties, known as cell annotation [e.g., Ergan et al. and Fischer et al.]
Conclusion: Impact of the HCA Collection
Dr. Jeremy Farrar, Chief Scientist, World Health Organization, said: "This landmark collection of papers from the international Human Cell Atlas community underscores the tremendous progress toward mapping every single kind of human cell and how they change as we grow up and age. The insights emerging from these discoveries are already reshaping our understanding of health and disease, paving the way for transformative health benefits that will impact lives worldwide."
Reference: "The Human Cell Atlas: towards a first draft atlas" 20 November 2024, Nature.
The individual studies in the Collection were funded by over one hundred different funding sources worldwide. The HCA also receives organizational support from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Wellcome, the Klarman Family Foundation, the Helmsley Charitable Trust, and others.
News
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]