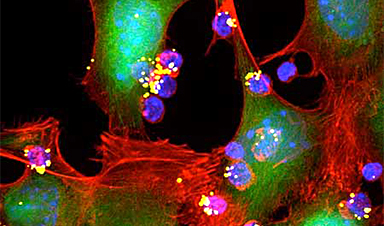
| Programming the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells has had promising results for treating blood cancers such as lymphoma and leukemia. This tactic has proven more challenging for solid tumors such as breast or lung cancers, but MIT researchers have now devised a novel way to boost the immune response against solid tumors. | |
| By developing nanoparticle “backpacks” that hold immune-stimulating drugs, and attaching them directly to T cells, the MIT engineers showed in a study of mice that they could enhance those T cells’ activity without harmful side effects. In more than half of the treated animals, tumors disappeared completely. | |
| “We found you could greatly improve the efficacy of the T cell therapy with backpacked drugs that help the donor T cells survive and function more effectively. Even more importantly, we achieved that without any of the toxicity that you see with systemic injection of the drugs,” says Darrell Irvine, a professor of biological engineering and of materials science and engineering, an associate director of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, and the senior author of the study. |
Image Credit: Yiran Zheng, MIT
News This Week
Nanomedicine in 2026: Experts Predict the Year Ahead
Progress in nanomedicine is almost as fast as the science is small. Over the last year, we've seen an abundance of headlines covering medical R&D at the nanoscale: polymer-coated nanoparticles targeting ovarian cancer, Albumin recruiting nanoparticles for [...]
Lipid nanoparticles could unlock access for millions of autoimmune patients
Capstan Therapeutics scientists demonstrate that lipid nanoparticles can engineer CAR T cells within the body without laboratory cell manufacturing and ex vivo expansion. The method using targeted lipid nanoparticles (tLNPs) is designed to deliver [...]
The Brain’s Strange Way of Computing Could Explain Consciousness
Consciousness may emerge not from code, but from the way living brains physically compute. Discussions about consciousness often stall between two deeply rooted viewpoints. One is computational functionalism, which holds that cognition can be [...]
First breathing ‘lung-on-chip’ developed using genetically identical cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and AlveoliX have developed the first human lung-on-chip model using stem cells taken from only one person. These chips simulate breathing motions and lung disease in an individual, [...]
Cell Membranes May Act Like Tiny Power Generators
Living cells may generate electricity through the natural motion of their membranes. These fast electrical signals could play a role in how cells communicate and sense their surroundings. Scientists have proposed a new theoretical [...]
This Viral RNA Structure Could Lead to a Universal Antiviral Drug
Researchers identify a shared RNA-protein interaction that could lead to broad-spectrum antiviral treatments for enteroviruses. A new study from the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), published in Nature Communications, explains how enteroviruses begin reproducing [...]
New study suggests a way to rejuvenate the immune system
Stimulating the liver to produce some of the signals of the thymus can reverse age-related declines in T-cell populations and enhance response to vaccination. As people age, their immune system function declines. T cell [...]
Nerve Damage Can Disrupt Immunity Across the Entire Body
A single nerve injury can quietly reshape the immune system across the entire body. Preclinical research from McGill University suggests that nerve injuries may lead to long-lasting changes in the immune system, and these [...]












Leave A Comment