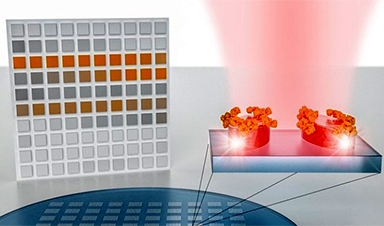
EPFL scientists have developed a unique system that can be used for detecting and analyzing molecules with very a level of high precision and without using any bulky equipment. This latest development paves the way for large-scale, image-based detection of materials assisted by artificial intelligence. The study has been reported in Science.
Organic compounds are typically detected and analyzed by infrared spectroscopy, but this method calls for complex procedures as well as huge and costly instruments which make device miniaturization quite difficult and thus limits its applications in certain medical and industrial applications and for collecting data out in the field, for example, for determining the concentrations of pollutants. Infrared spectroscopy is also essentially restricted by low sensitivities and thus needs large amounts of samples.
Conversely, a research team from EPFL’s School of Engineering and Australian National University (ANU) has designed a sensitive and compact nanophotonic system that is capable of identifying the absorption characteristics of a molecule without using traditional spectrometry. The researchers have already detected organic compounds, polymers, and pesticides with their system, which can also be used with CMOS technology.
The novel system features an engineered surface which is surrounded with countless numbers of very small sensors known as metapixels. These metapixels can create a unique bar code for each molecule that the surface comes into contact, and using advanced pattern recognition and sorting technology (for example, artificial neural networks) these bar code can be extensively analyzed. This study – which turns out to be a meeting point of nanotechnology, physics, and big data – has been reported in the Science journal.
Image Credit: © 2018 EPFL
News This Week
Scientists Have Discovered Toxic “Forever Chemicals” in Bottled Water
Scientists have found toxic PFAS in drinking water samples from around the world, with higher levels in tap water from China compared to the UK. Boiling water or using a filtration jug can reduce [...]
Urban Microbes Are Eating Disinfectants – Are We Fueling a New Health Threat?
New research reveals that microbes in urban environments are evolving to withstand the very cleaning agents designed to eliminate them. The study also uncovers new strains in Hong Kong, previously only found in the [...]
Startling Study Shows High-Potency Cannabis Alters DNA
The study shows that frequent use of high-potency cannabis alters DNA, affecting genes related to energy and immune function. These changes differ between those with and without psychosis, suggesting cannabis use could influence mental health through biological [...]
New nanotherapy targets artery inflammation in cardiovascular disease
Inflammation of the arteries is a primary precursor and driver of cardiovascular disease—the No. 1 killer of people in the United States. This inflammation is associated with the buildup of dangerous plaque inside the [...]
Revolutionary Nanoparticle Therapy for Prostate Cancer
A groundbreaking research effort involving teams from the University of Virginia, Mount Sinai, the University of Michigan, the University of Texas, and others has displayed the clinical efficacy of an innovative therapy that utilizes nanoparticles and [...]
Antibody engineering drives innovation in drug development
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are used to prevent, detect, and treat a broad spectrum of non-communicable and communicable diseases. Over the past few years, the market for mAbs has grown exponentially with an expected compound [...]
Breakthrough Study Reveals How Bladder Cancer Starts and Spreads
Researchers found that DNA mutations from antiviral enzymes and chemotherapy fuel early bladder cancer, while abnormal circular DNA in tumor cells drives resistance to therapy. These discoveries open new therapeutic avenues. A groundbreaking study led by [...]
AI and Quantum Mechanics Accelerate Drug Discovery
A recent article published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling researchers at Southern Methodist University (SMU) have developed SmartCADD, an open-source virtual tool designed to speed [...]










Leave A Comment