Stefan Wilhelm, an associate professor in the Stephenson School of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, and several students in his Biomedical Nano-Engineering Lab have recently published an article in the journal Nano Letters that outlines their recent important nanomedicine advancement.
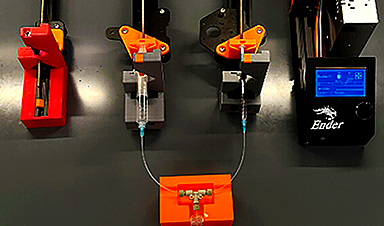
Wilhelm, with student researchers such as Hamilton Young, a senior biomedical engineering student, and Yuxin He, a biomedical engineering graduate research assistant, used 3D printer parts to mix fluid streams together containing the building blocks of nanomedicines and their payloads in a T-mixer format.
“This mixing device is essentially a T-shaped piece of tubing that forces two fluid streams to flow into each other, mixing nanomaterial and payload components together. Once mixed, the final product would exit through the other end,” Wilhelm said. “This mixing concept is used in industrial processes, so we wondered if we could make these devices as cost-efficient as possible.”
The team discovered a publication from a European research group that demonstrated that commercially available 3D printers could be reassembled into syringe pumps needed to push the fluids through the T-mixer device. Once built, they tried to produce nanomedicines with their 3D-built T-mixer.
“We were focusing on formulations that are used in the clinic, such as mRNA lipid nanoparticles, liposomes, and polymeric nanoparticles. One of the molecules we used was developed by a collaborator at OU Health Sciences to limit prostate cancer cell growth,” Wilhelm said. “We encapsulated this molecule into our nanomedicine formulations and showed that it actually stops those prostate cancer cells from growing.”

Based on this example, the team’s research has potentially broad implications for novel cancer therapies and vaccines against infectious diseases, as mRNA technology is already being used in clinical trials for personalized cancer vaccines.
“All of this mRNA technology relies on nanotechnology. mRNA molecules degrade too fast in the body to be effective without encapsulating them in nanoparticles,” Wilhelm said. “This process could open up a bright future for nanotechnology in medicine and will hopefully greatly improve health care.”
Wilhelm also foresees a future where doctors’ offices and clinics in rural communities with limited resources could use this technology to create personalized vaccines. His work with B4NANO, a partnership and outreach program with Native American tribes and communities in Oklahoma, inspires this goal.
“I could see a future situation where a patient walks into a doctor’s office with an infectious disease —possibly cancer. After a diagnosis by the doctor, a vaccine is produced at the doctor’s office in a manner similar to how a single-serve coffee maker works—you just put in your capsules, press a button, and get a personalized vaccine for that patient,” Wilhelm said. “Our goal is to develop this kind of benchtop device and then hopefully find industry partners to commercialize systems like these.”
Another goal Wilhelm has is training the next generation of biomedical engineers, like Young and He, to solve challenges in health care.
“The challenges we face in biomedical engineering require that we have a diverse team, with people coming from all different kinds of backgrounds. Everybody brings in their unique perspective, unique skill sets,” Wilhelm said. “My lab places a lot of emphasis on working with undergraduate students, even high school students, and bridging the gap from undergraduates to graduate students to postdocs. They learn from each other and learn to mentor each other.”
More information: Hamilton Young et al, Toward the Scalable, Rapid, Reproducible, and Cost-Effective Synthesis of Personalized Nanomedicines at the Point of Care, Nano Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04171
News
The Global Nanomedicine Market: Key Players and Emerging Technologies in Healthcare
This article provides an overview of the global nanomedicine market, highlighting key players, emerging technologies, and the challenges and opportunities that influence its growth and commercialization in the healthcare sector. Nanomedicines are nanotechnology-based drug products [...]
Scientists Have Discovered Toxic “Forever Chemicals” in Bottled Water
Scientists have found toxic PFAS in drinking water samples from around the world, with higher levels in tap water from China compared to the UK. Boiling water or using a filtration jug can reduce [...]
Urban Microbes Are Eating Disinfectants – Are We Fueling a New Health Threat?
New research reveals that microbes in urban environments are evolving to withstand the very cleaning agents designed to eliminate them. The study also uncovers new strains in Hong Kong, previously only found in the [...]
Startling Study Shows High-Potency Cannabis Alters DNA
The study shows that frequent use of high-potency cannabis alters DNA, affecting genes related to energy and immune function. These changes differ between those with and without psychosis, suggesting cannabis use could influence mental health through biological [...]
New nanotherapy targets artery inflammation in cardiovascular disease
Inflammation of the arteries is a primary precursor and driver of cardiovascular disease—the No. 1 killer of people in the United States. This inflammation is associated with the buildup of dangerous plaque inside the [...]
Revolutionary Nanoparticle Therapy for Prostate Cancer
A groundbreaking research effort involving teams from the University of Virginia, Mount Sinai, the University of Michigan, the University of Texas, and others has displayed the clinical efficacy of an innovative therapy that utilizes nanoparticles and [...]
Antibody engineering drives innovation in drug development
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are used to prevent, detect, and treat a broad spectrum of non-communicable and communicable diseases. Over the past few years, the market for mAbs has grown exponentially with an expected compound [...]
Breakthrough Study Reveals How Bladder Cancer Starts and Spreads
Researchers found that DNA mutations from antiviral enzymes and chemotherapy fuel early bladder cancer, while abnormal circular DNA in tumor cells drives resistance to therapy. These discoveries open new therapeutic avenues. A groundbreaking study led by [...]
AI and Quantum Mechanics Accelerate Drug Discovery
A recent article published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling researchers at Southern Methodist University (SMU) have developed SmartCADD, an open-source virtual tool designed to speed [...]
Targeting ‘undruggable’ diseases: Researchers reveal new levels of detail in targeted protein degradation
Researchers at the University of Dundee have revealed in the greatest detail yet the workings of molecules called protein degraders which can be deployed to combat what have previously been regarded as "undruggable" diseases, [...]
Revolutionizing Virology: AI Discovers Over 160,000 New RNA Viruses
Largest discovery of new virus species sheds light on the hidden virosphere. Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used to reveal details of a diverse and fundamental branch of life living right under our feet and in every [...]
Cardiac Crisis: COVID-19 Doubles Risk of Heart Attacks, Strokes, and Death
Research indicates that COVID-19 survivors face doubled risks of severe cardiac events for years after recovery, especially if hospitalized. People with A, B, or AB blood types are particularly vulnerable, highlighting the need for personalized approaches [...]
AI steps into science limelight with Nobel wins
For long periods of its history, artificial intelligence has lurked in the hinterland of science, often unloved and unfunded—but two Nobel prizes in one week suggest its time in the sunshine has finally arrived. [...]
MIT Scientists Shed New Light on the Critical Brain Connections That Define Consciousness
A new study provides further evidence that consciousness depends on communication between the brain’s sensory and cognitive regions in the cortex. Our brains are constantly making predictions about our surroundings, enabling us to focus [...]
Common Chemicals Found in Shampoo and Plastic Could Be Quietly Disrupting Your Heart’s Rhythm
UC study of Fernald data links environmental phenols to heart toxicities Environmental phenols are present in numerous everyday consumer products, serving as preservatives in packaged foods, parabens in shampoos, and bisphenol A (BPA) in [...]
Revolutionary Brain Tech Offers New Hope for Stroke and Injury Recovery
University of Pittsburgh researchers report that deep brain stimulation (DBS) can effectively enhance motor functions in individuals with arm and hand paralysis due to brain injuries, with promising results from early human and monkey [...]