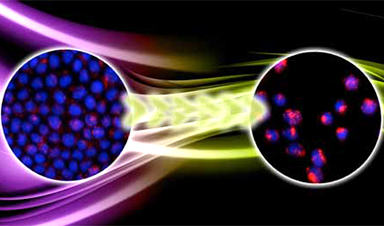
| Diseased cells such as metastatic cancer cells have markedly different mechanical properties that can be used to improve targeted drug uptake, according to a team of researchers at Penn State. | |
| Many labs around the world are developing nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems to selectively target tumors. They rely on a key-and-lock system in which protein keys on the surface of the nanoparticle click into the locks of a highly expressed protein on the surface of the cancer cell. The cell membrane then wraps around the nanoparticle and ingests it. If enough of the nanoparticles and their drug cargo is ingested, the cancer cell will die. | |
| The adhesive force of the lock and key is what drives the nanoparticle into the cell, says Sulin Zhang, professor of engineering science and mechanics. “It is almost universal that whenever there is a driving force for a process, there always is a resistive force. Here, the driving force is biochemical – the protein-protein interaction.” | |
| The resistive force is mechanical, the energy cost of the membrane wrapping around the nanoparticle. Until now, bioengineers only considered the driving force and designed nanoparticles to optimize the chemical interactions, a targeting strategy called “chemotargeting.” Zhang believes they should also take into account the mechanics of the cells to design nanoparticles to achieve enhanced targeting, which forms a new targeting strategy called “mechanotargeting.” |
Image Credit: Zhang lab/vecteezy.com
News This Week
Urban Microbes Are Eating Disinfectants – Are We Fueling a New Health Threat?
New research reveals that microbes in urban environments are evolving to withstand the very cleaning agents designed to eliminate them. The study also uncovers new strains in Hong Kong, previously only found in the [...]
Startling Study Shows High-Potency Cannabis Alters DNA
The study shows that frequent use of high-potency cannabis alters DNA, affecting genes related to energy and immune function. These changes differ between those with and without psychosis, suggesting cannabis use could influence mental health through biological [...]
New nanotherapy targets artery inflammation in cardiovascular disease
Inflammation of the arteries is a primary precursor and driver of cardiovascular disease—the No. 1 killer of people in the United States. This inflammation is associated with the buildup of dangerous plaque inside the [...]
Revolutionary Nanoparticle Therapy for Prostate Cancer
A groundbreaking research effort involving teams from the University of Virginia, Mount Sinai, the University of Michigan, the University of Texas, and others has displayed the clinical efficacy of an innovative therapy that utilizes nanoparticles and [...]
Antibody engineering drives innovation in drug development
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are used to prevent, detect, and treat a broad spectrum of non-communicable and communicable diseases. Over the past few years, the market for mAbs has grown exponentially with an expected compound [...]
Breakthrough Study Reveals How Bladder Cancer Starts and Spreads
Researchers found that DNA mutations from antiviral enzymes and chemotherapy fuel early bladder cancer, while abnormal circular DNA in tumor cells drives resistance to therapy. These discoveries open new therapeutic avenues. A groundbreaking study led by [...]
AI and Quantum Mechanics Accelerate Drug Discovery
A recent article published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling researchers at Southern Methodist University (SMU) have developed SmartCADD, an open-source virtual tool designed to speed [...]
Targeting ‘undruggable’ diseases: Researchers reveal new levels of detail in targeted protein degradation
Researchers at the University of Dundee have revealed in the greatest detail yet the workings of molecules called protein degraders which can be deployed to combat what have previously been regarded as "undruggable" diseases, [...]









Leave A Comment